Nestled in the heart of Boston, Trinity Church stands not merely as a place of worship but as a living testament to the city’s historical and architectural tapestry.
Since its establishment in 1733, this Episcopal masterpiece has weathered the sands of time, evolving through centuries of societal shifts and cultural transitions.
Designed by the eminent Henry Hobson Richardson and completed in 1877, Trinity Church is a beacon of Richardsonian Romanesque brilliance.
Its rich history encompasses art, spirituality, and community, weaving a narrative that transcends ecclesiastical boundaries.
Join us on a journey through the history of trinity church Boston, where each stone tells a story, and each arch whispers tales of resilience, creativity, and enduring significance.
History Of Trinity Church Boston
Trinity Church in Boston stands as an architectural masterpiece and a symbol of the city’s rich history.
Let’s delve into some historical milestones that encapsulate the journey of Trinity Church and its profound impact on Boston’s cultural and religious landscape.
Founding and Early Years (1733)
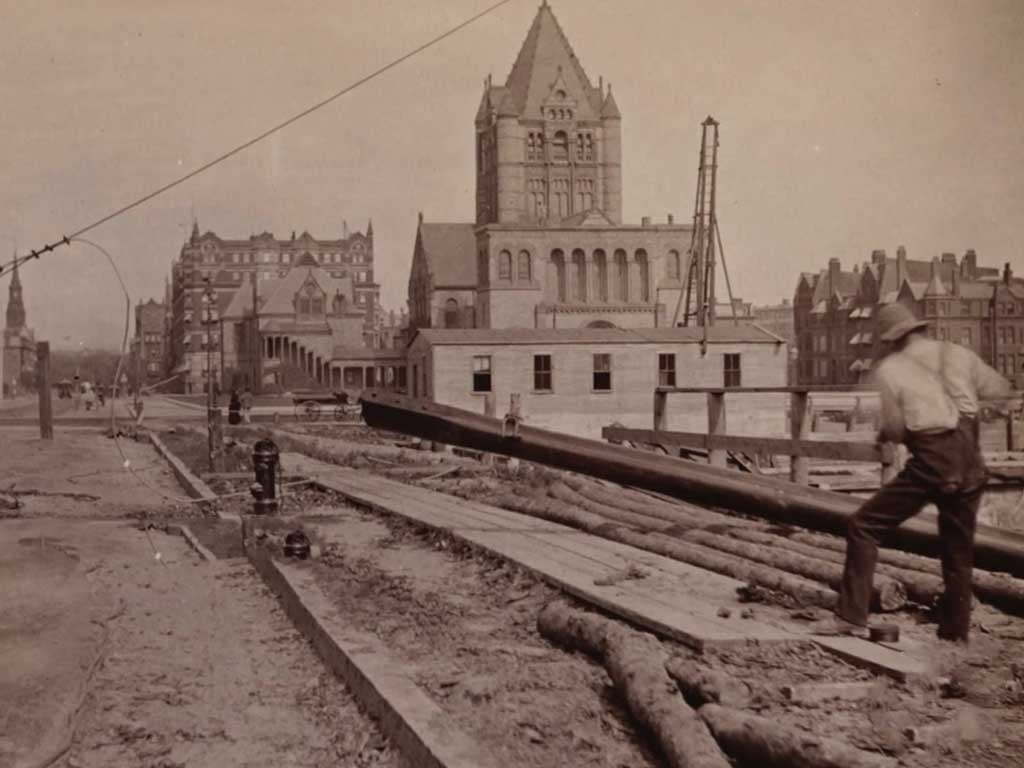

Trinity Church traces its roots back to 1733 when a group of Anglicans established the King’s Chapel. The first structure, completed in 1735, laid the foundation for what would evolve into Trinity Church, marking the earliest chapter in its storied history.
Construction of the Current Building (1877-1879)
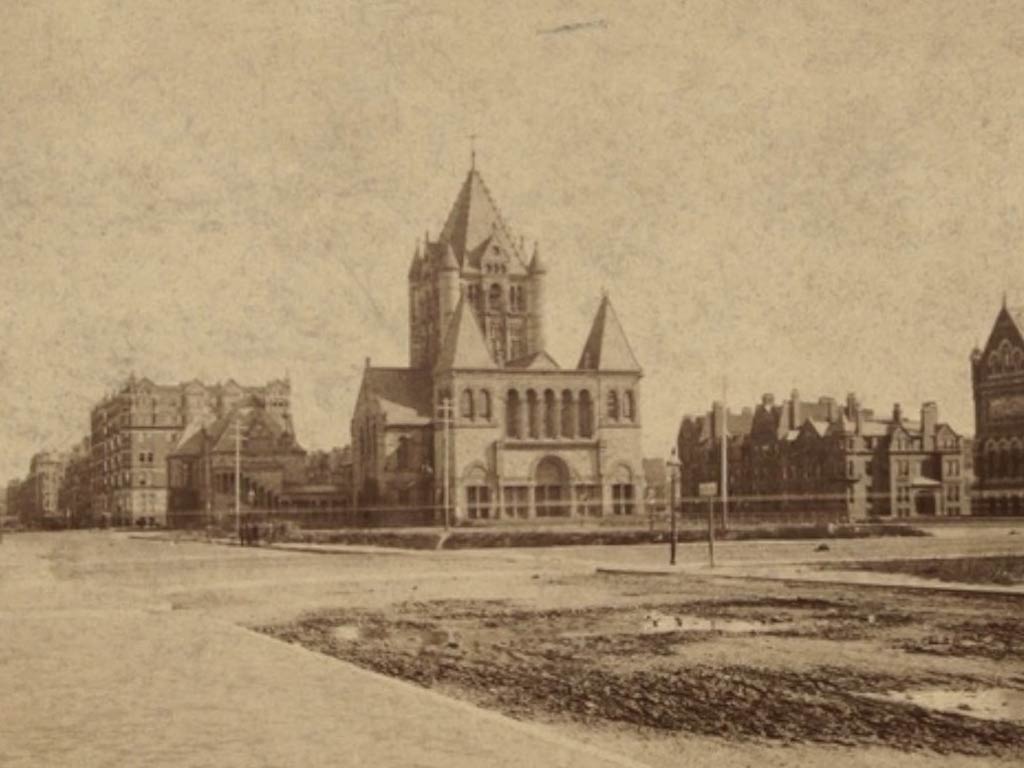

The iconic Richardsonian Romanesque-style building, designed by architect Henry Hobson Richardson, was constructed between 1877 and 1879.
This architectural gem, characterized by its distinctive red sandstone and intricate carvings, replaced the original structure and solidified Trinity Church as a cultural landmark.
Role in the American Arts and Crafts Movement (Late 19th Century)
Trinity Church played a pivotal role in the American Arts and Crafts Movement, hosting the Boston Society of Arts and Crafts exhibitions.
The church’s commitment to fostering artistic expression and creativity added a cultural dimension to its historical significance during the late 19th century.
H.H. Richardson’s Influence (Late 19th Century)
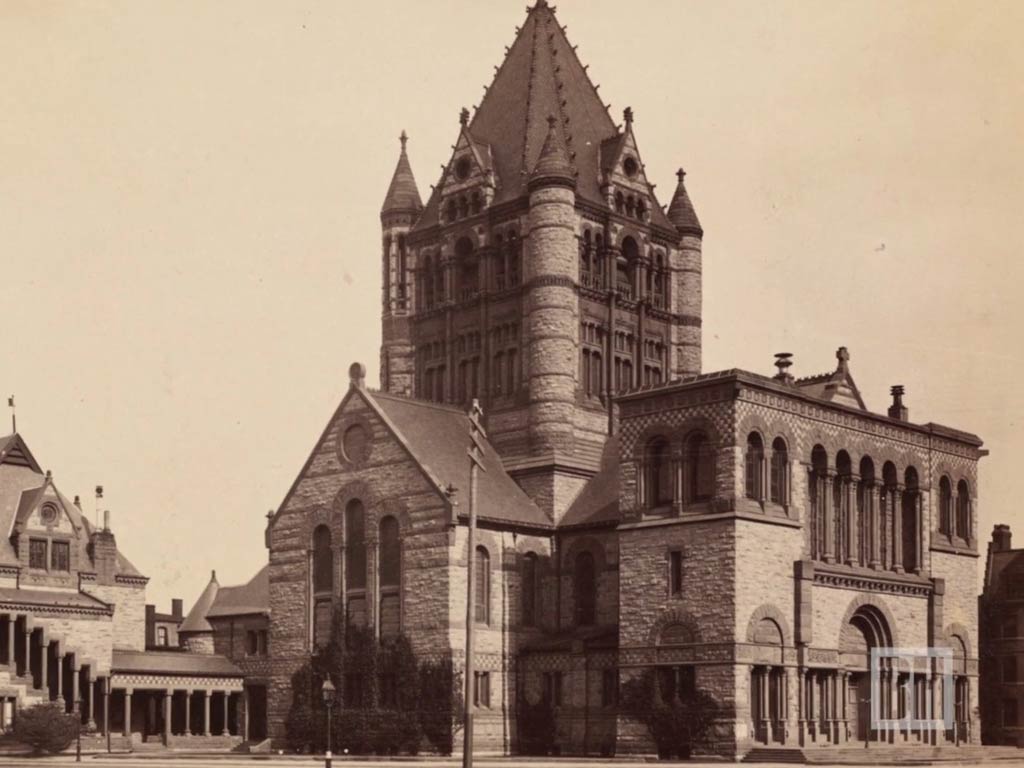

Architect H.H. Richardson’s innovative design not only defined Trinity Church’s visual identity but also influenced American architecture.
The church became a focal point for showcasing Richardson’s Romanesque style, leaving an enduring legacy in the architectural landscape of Boston and beyond.
National Historic Landmark Designation (1970)
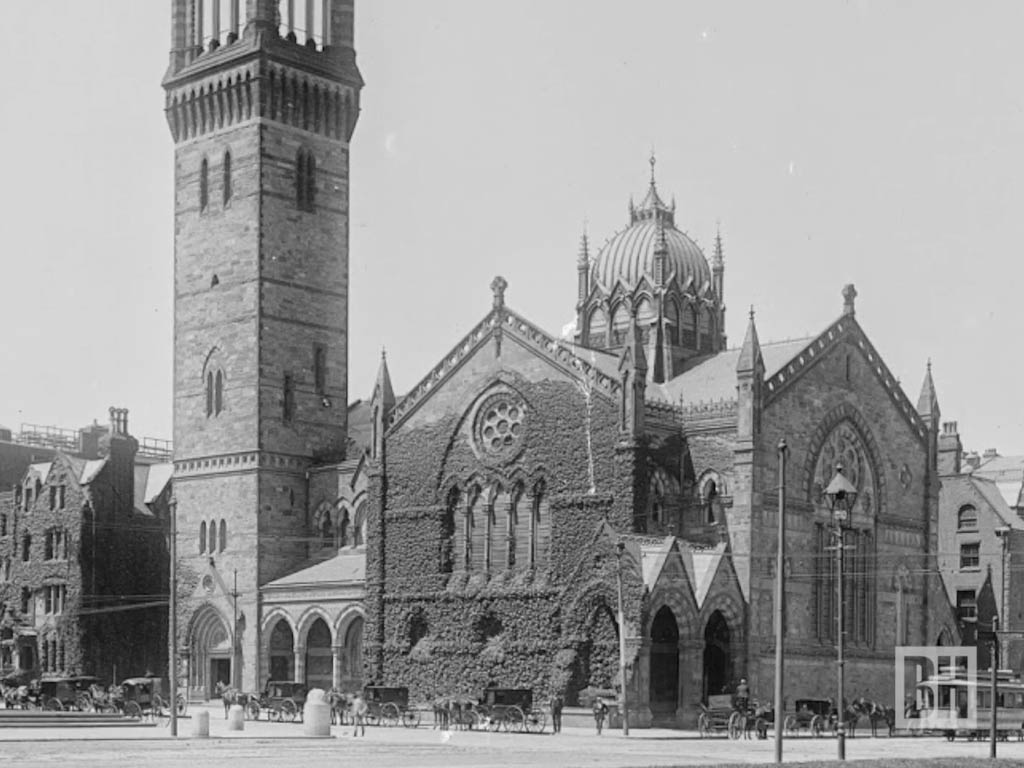
In recognition of its architectural significance, Trinity Church was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1970.
This acknowledgment affirmed its status as a cultural and historical treasure, drawing visitors and scholars alike to explore its captivating narrative and intricate design.
The Tiffany Windows (Late 19th Century)
Trinity Church became renowned for its stunning stained glass windows designed by Louis Comfort Tiffany.
Installed between 1877 and 1930, these intricate windows, including the “John La Farge” window, added a mesmerizing visual and spiritual dimension to the church’s interior.
The Merger with St. John’s Church (1910)

In 1910, Trinity Church merged with St. John’s Church, expanding its congregational reach. This union further solidified Trinity Church’s commitment to fostering community and spiritual growth, marking a significant chapter in its ecclesiastical journey.
Preservation Efforts and Renovations (20th century)
Throughout the 20th century, Trinity Church underwent preservation efforts to maintain its architectural integrity.
Renovations, including the restoration of murals and the addition of modern amenities, ensured that the church retained its historical charm while adapting to contemporary needs.
The Centennial Celebration (1977)
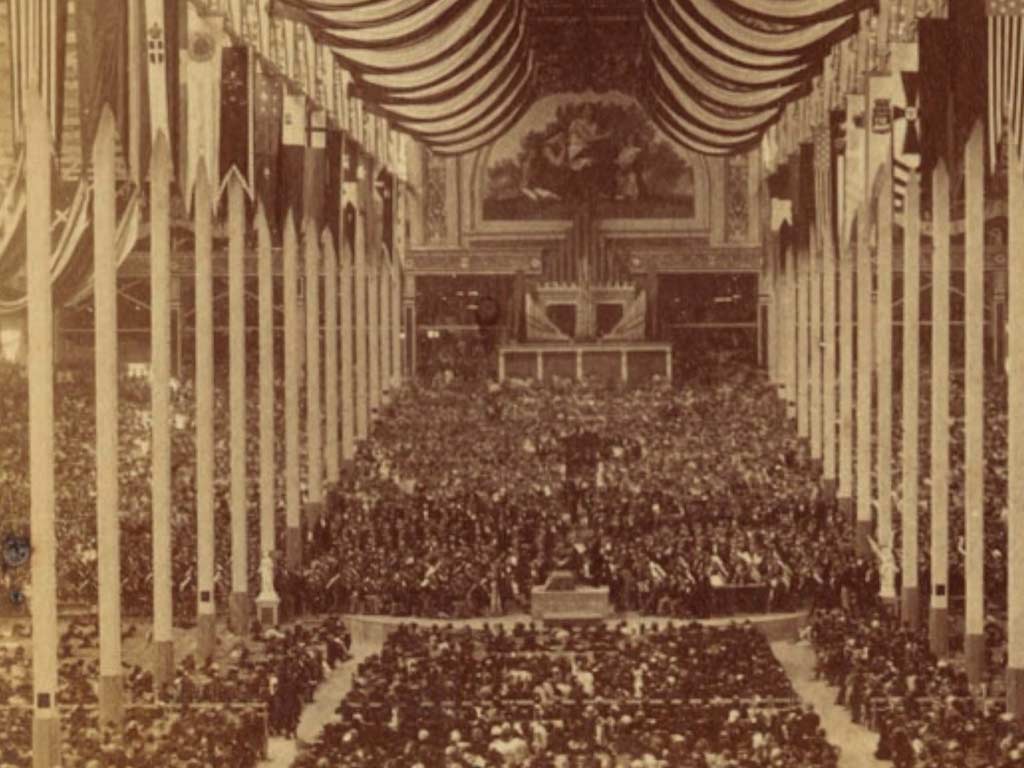
Trinity Church celebrated its bicentennial in 1977, marking 200 years since its founding. The centennial celebrations included special events, exhibitions, and reflections on the church’s profound impact on Boston’s cultural, religious, and architectural landscape.
Recognition as “America’s Favorite Architecture” (2007)
Trinity Church garnered national acclaim in 2007 when the American Institute of Architects recognized it as one of “America’s Favorite Architecture.”
This acknowledgment highlighted the enduring appeal and architectural significance of Trinity Church on a broader scale.
The Music Program’s Ascendancy (20th century)
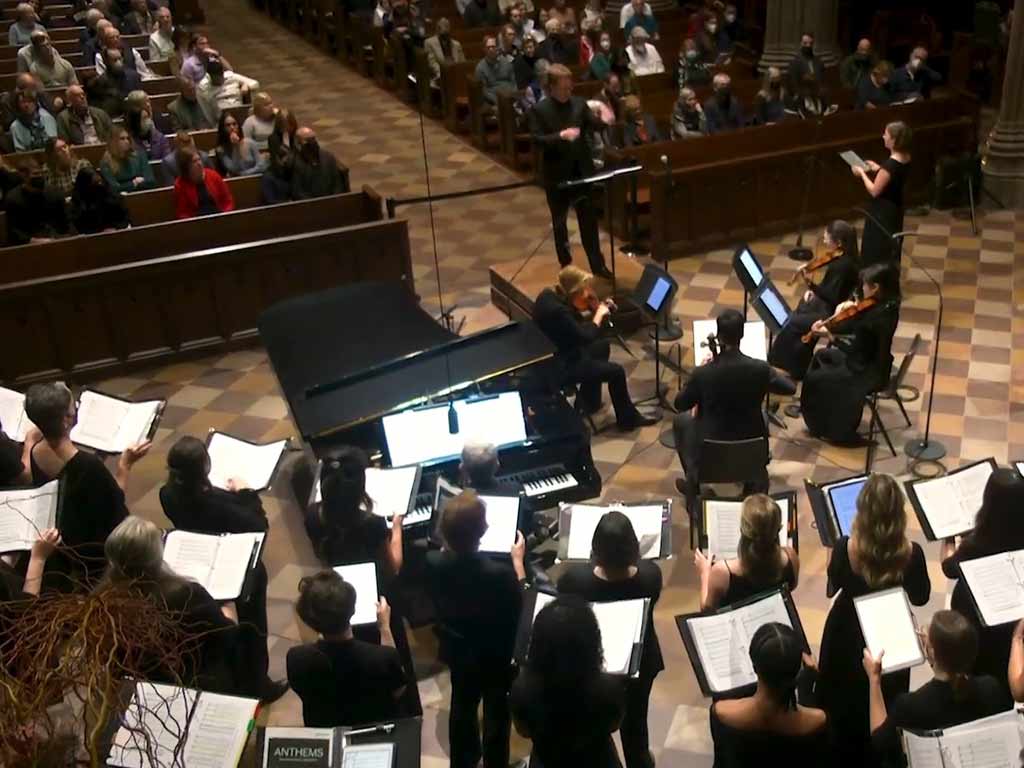

In the 20th century, Trinity Church’s music program rose to prominence. The church became a hub for musical excellence, hosting concerts, choirs, and events that enriched Boston’s cultural landscape and fostered a deep appreciation for the intersection of spirituality and music.
Interfaith Engagement and Social Justice Initiatives (21st century)
Trinity Church has embraced interfaith dialogue and social justice initiatives in the 21st century. Through collaborative efforts with diverse religious communities and impactful social programs, the church has expanded its role beyond ecclesiastical boundaries, embodying a commitment to inclusivity and community service.
The Tower Restoration Project (2010)
The Tower Restoration Project, initiated in 2010, aimed to preserve and restore Trinity Church’s iconic tower.
This project not only ensured the structural integrity of the church but also reaffirmed its commitment to maintaining its historic allure for future generations.
The Green Spaces Initiative (2021)
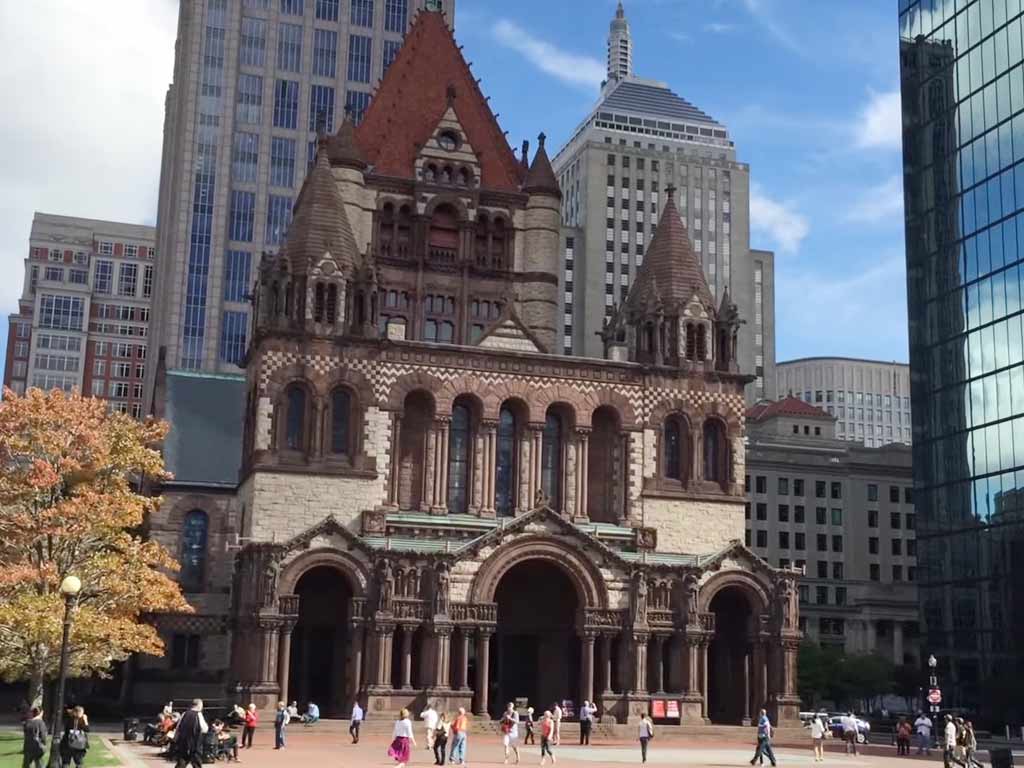

In 2021, Trinity Church launched the Green Spaces Initiative, focusing on enhancing the church’s surrounding outdoor areas.
This initiative reflects a dedication to creating inviting, sustainable spaces that contribute to the well-being of both congregants and the broader Boston community.
Adaptive Reuse and Community Hub (Ongoing)
Trinity Church continues to adapt to contemporary needs by transforming spaces within its campus for community use. This ongoing initiative reflects a commitment to providing a welcoming environment that serves as not only a religious sanctuary but also a vibrant community hub.
Trinity Church’s history is a dynamic narrative that extends well beyond its architectural splendor.
From music excellence to interfaith engagement and modern initiatives, each historical landmark showcases the church’s enduring commitment to spirituality, cultural enrichment, and community betterment.
How Did The Boston Trinity Church Change Architecture In The United States?
Trinity Church in Boston, a quintessential example of Richardsonian Romanesque architecture, holds a unique place in the history of American architecture.
Here are some ways in which Trinity Church in Boston changed the architectural landscape:
Revival of Romanesque Style
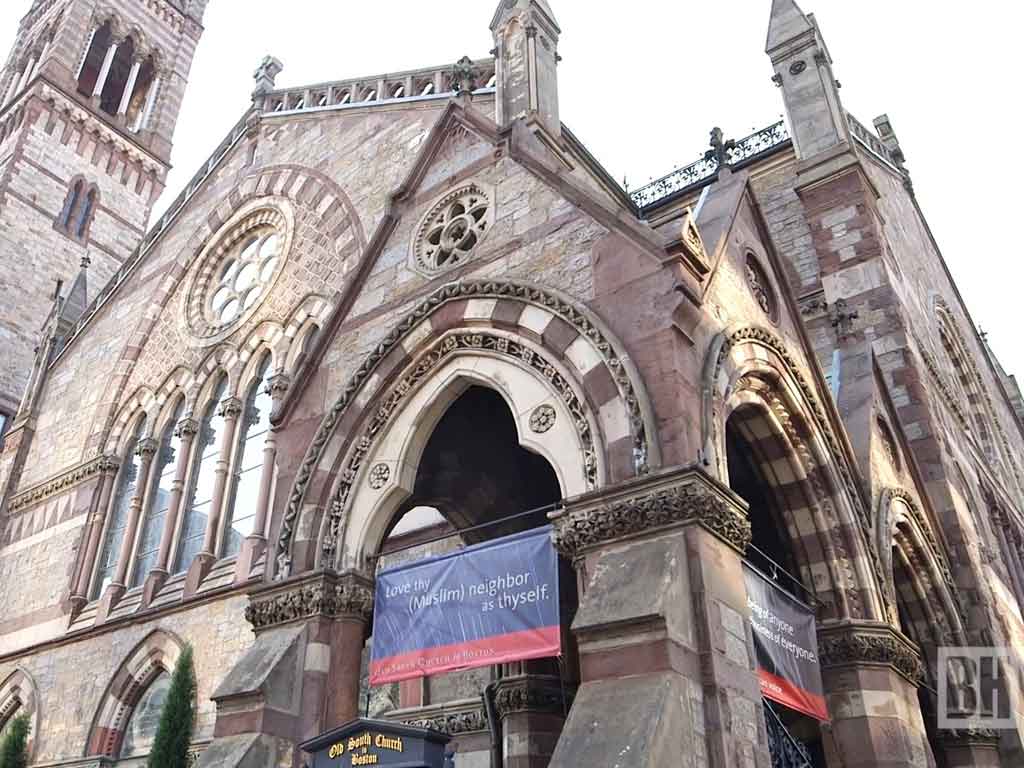

Trinity Church’s Richardsonian Romanesque style marked a departure from prevailing architectural trends, reviving the Romanesque style’s robust, fortress-like characteristics.
This departure challenged the dominance of Gothic architecture and inspired a renewed interest in the Romanesque across the United States, influencing subsequent architectural choices.
Integration of Arts and Crafts Movement
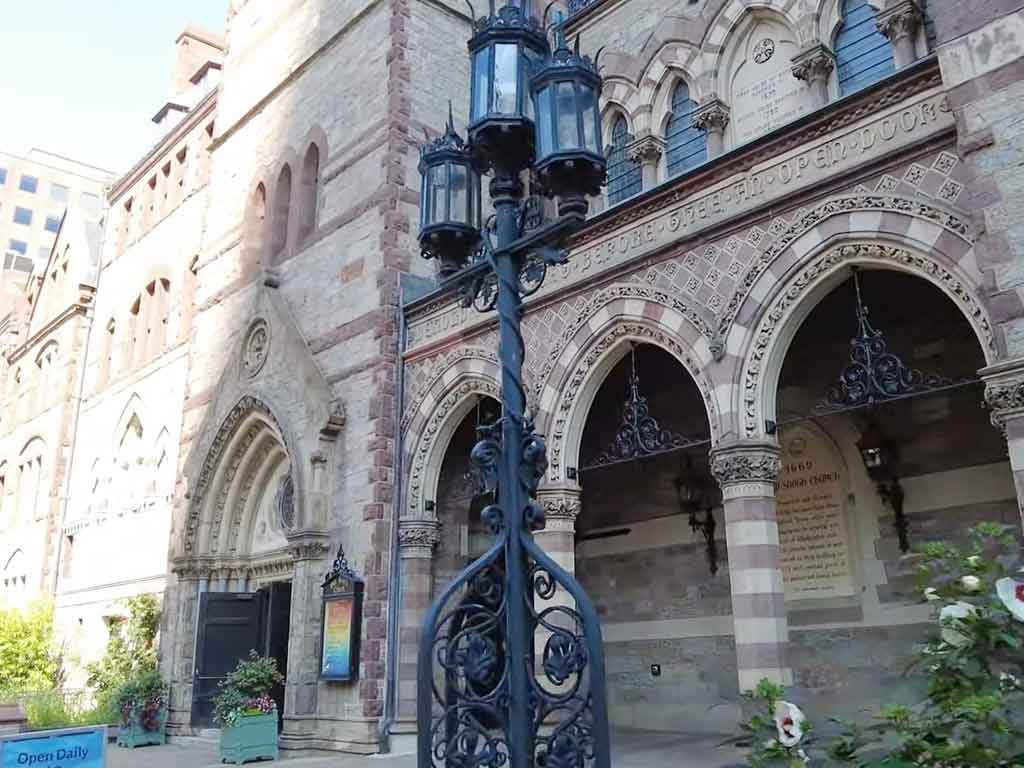

Trinity Church played a pivotal role in the American Arts and Crafts Movement, with its interior adorned by masterpieces from renowned artists like John La Farge and Louis Comfort Tiffany.
This integration of fine arts within architectural design became a hallmark, contributing to the broader Arts and Crafts Movement’s influence on American design principles.
Innovative Use of Materials
Richardson’s design for Trinity Church showcased an innovative use of materials, including contrasting layers of sandstone and intricate carvings. This approach to materials was groundbreaking, influencing architects to experiment with diverse materials in their designs.
Trinity Church’s use of textured materials set a precedent for creative material application in American architecture.
Emphasis on Craftsmanship
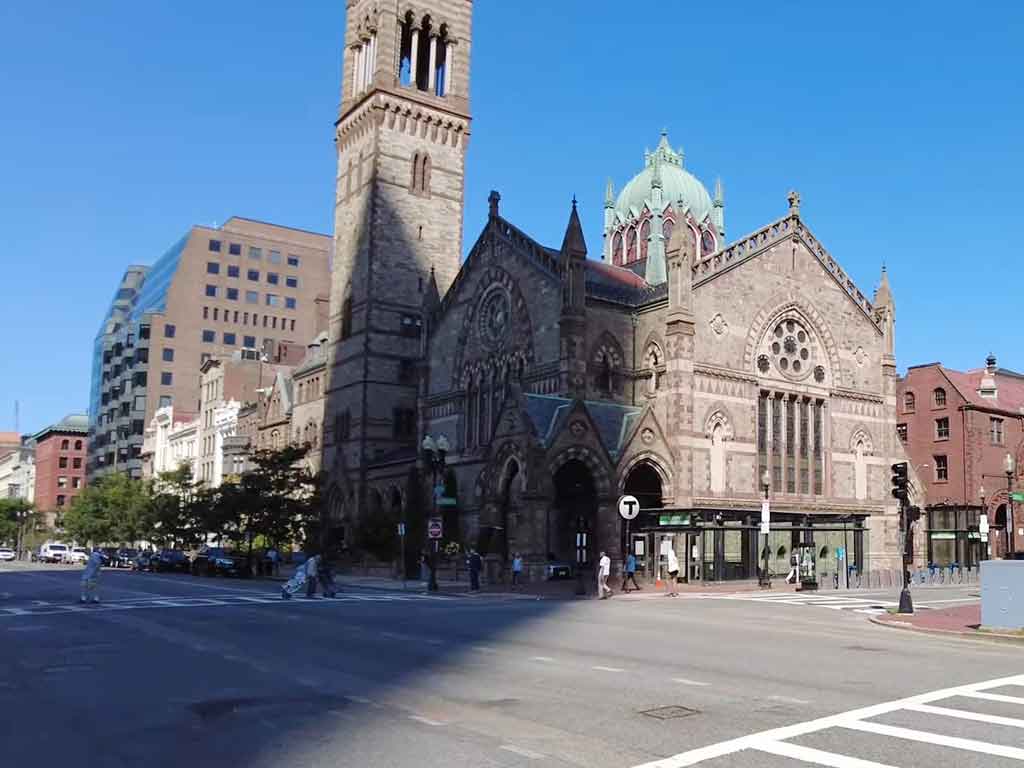

The meticulous craftsmanship displayed in Trinity Church’s construction elevated the significance of artisanal work.
This emphasis on craftsmanship became a hallmark of Richardsonian Romanesque architecture, fostering a renewed appreciation for skilled labor and influencing architects to prioritize the quality of craftsmanship in their projects.
Architectural Regionalism
Trinity Church contributed to the rise of architectural regionalism, as its design reflected a departure from European influences. By drawing inspiration from regional historical elements, Richardson’s work at Trinity Church established a uniquely American architectural identity.
This departure from European styles encouraged architects to explore and celebrate indigenous design influences.
Trinity Church in Boston, through its Richardsonian Romanesque design and integration of artistic elements, ushered in a paradigm shift in American architecture.
The ripple effects of its innovative approach can be traced through subsequent architectural movements, leaving an indelible mark on the nation’s built environment.
Influence on Subsequent Church Designs
Trinity Church’s distinctive architectural elements, such as its Richardsonian Romanesque arches and robust stone construction, became influential in church design nationwide.
Houses of worship across the United States adopted similar features, reflecting the enduring impact of Trinity Church on ecclesiastical architecture.
Shift towards Monumental Architecture
The grandeur and scale of Trinity Church marked a shift towards monumental architecture in the United States.
Richardson’s vision for a commanding yet harmonious structure inspired architects to conceive buildings that conveyed a sense of permanence and aesthetic grandiosity, shaping the American architectural ethos.
Foundations of Urban Planning
Trinity Church’s placement within Copley Square underscored the importance of thoughtful urban planning. The church became a central focal point, contributing to the emergence of well-designed public spaces in American cities.
This emphasis on urban aesthetics influenced subsequent city planning endeavors, prioritizing the integration of architectural landmarks.
Evolution of Richardsonian Romanesque in Public Buildings
Trinity Church served as a catalyst for the widespread adoption of Richardsonian Romanesque in public buildings. The style became synonymous with solidity, texture, and visual appeal.
Public structures, including libraries, courthouses, and city halls, embraced Richardson’s design principles, creating a distinctive architectural identity for civic buildings.
Legacy of Henry Hobson Richardson
Trinity Church solidified Henry Hobson Richardson’s legacy as a pioneer of American architecture.
The success of this project catapulted Richardson to architectural prominence, and his Richardsonian Romanesque style continued to influence architects like Frank Lloyd Wright and Louis Sullivan.
Trinity Church thus became a cornerstone in Richardson’s enduring impact on the American architectural panorama.
Trinity Church’s architectural influence extends beyond its walls, permeating the very fabric of American design philosophy.
From sacred spaces to civic structures, its Richardsonian Romanesque legacy and urban planning principles have left an indelible imprint on the nation’s architectural narrative.
FAQs
Who designed Trinity Church, and when was it built?
Designed by Henry Hobson Richardson, Trinity Church was constructed between 1877 and 1879. Richardson’s innovative Richardsonian Romanesque style left an indelible mark on American architecture.
How has the Trinity Church influenced American architecture?
Trinity Church profoundly impacted American architecture by popularizing Richardsonian Romanesque, influencing subsequent church designs, and contributing to the emergence of monumental architecture.
What role did Trinity Church play in the Arts and Crafts Movement?
Trinity Church played a pivotal role in the American Arts and Crafts Movement by hosting exhibitions and integrating masterpieces from artists like John La Farge and Louis Comfort Tiffany.
How has Trinity Church adapted to contemporary needs?
Trinity Church has adapted to contemporary needs through preservation efforts, restorations, and initiatives like the Green Spaces Initiative, reflecting a commitment to maintaining historical charm while catering to modern requirements.
What is Trinity Church’s legacy and impact on Boston?
Trinity Church’s legacy extends beyond its religious role it’s a cultural landmark, an architectural masterpiece, and a symbol of Boston’s endurance. Its impact can be seen in urban planning, public spaces, and the evolution of American architecture.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the history of Trinity Church in Boston, the echoes of centuries past reverberate within its hallowed walls.
From its humble beginnings in the 18th century to becoming an iconic architectural gem in the 19th, Trinity Church stands as a testament to the city’s endurance and adaptability.
Its history intertwines with Boston’s narrative, shaping not only the spiritual landscape but also influencing American architecture. Trinity Church beckons as more than a physical structure; it is a repository of collective memories, an artistic marvel, and a symbol of cultural evolution.
In its history, we find not only the chronicles of a place of worship but a chronicle of Boston itself a city that, like Trinity Church, has gracefully embraced change while preserving its timeless essence.
Jaclyn Lowe