The history of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) unfolds as a dynamic narrative intricately woven into the fabric of Greater Boston’s evolution.
Established in 1964, the MBTA has been a cornerstone of the region’s public transportation landscape, connecting communities, shaping urban development, and adapting to the changing needs of a burgeoning metropolis.
From its foundational consolidation of disparate transit services to pivotal expansions, technological innovations, and responses to contemporary challenges, the MBTA’s journey mirrors the growth and resilience of the communities it serves.
This retrospective journey through the history of the MBTA unveils the authority’s enduring commitment to providing accessible, efficient, and sustainable transit solutions that have become integral to the daily lives of millions.

When Did The MBTA Start?
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA), commonly known as the “T,” began its operations on September 1, 1964.
This public transportation agency was established to consolidate and manage various privately operated transit services serving the Greater Boston region.
The MBTA’s formation marked a significant step toward creating a unified and efficient public transportation system for the metropolitan area.
Over the years, the MBTA has expanded its network, encompassing buses, commuter rail, ferries, and the iconic subway system, known as the “Green Line,” becoming a vital lifeline for residents and visitors alike in the Greater Boston area.
What Does MBTA Stand For?
The acronym MBTA stands for the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority, a pivotal agency overseeing public transportation in the Greater Boston area.
Established in 1964, the MBTA plays a crucial role in providing efficient and comprehensive transit services, including buses, commuter rail, ferries, and subway systems.
Serving as the backbone of the region’s transportation infrastructure, the MBTA facilitates the daily commute for millions of residents, students, and workers.
Its commitment to accessibility, environmental sustainability, and connectivity reflects its integral role in enhancing mobility and fostering community well-being across the diverse urban and suburban landscapes of Eastern Massachusetts.
History Of The MBTA
The history of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA), colloquially known as the “T,” is a journey intertwined with the evolution of Greater Boston’s public transit.
Here are some historical milestones that underscore the significance of the MBTA in connecting communities and facilitating transportation.:
Founding and Consolidation (1964)
The MBTA was established on August 3, 1964, as a response to the need for a unified, efficient public transportation system in the Greater Boston area.
This marked the consolidation of various privately operated transit services under a single authority, heralding a new era in the region’s transportation infrastructure.
Introduction of the Red Line (1965)
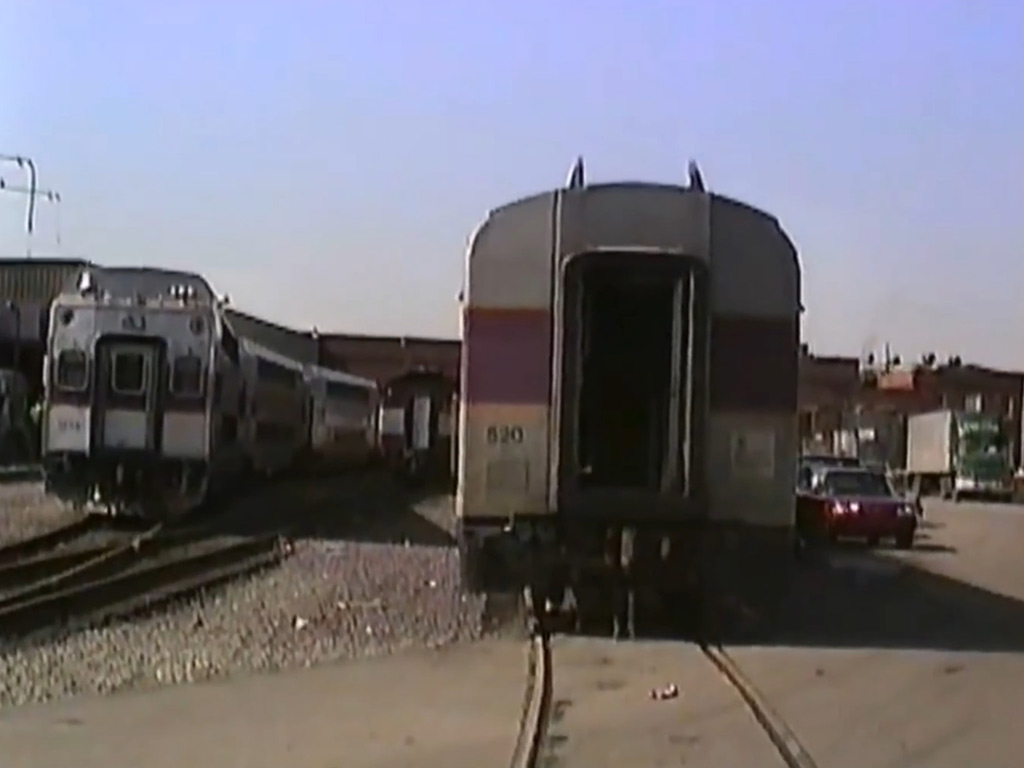

The Red Line, one of the MBTA’s rapid transit lines, made its debut on March 23, 1965, connecting Cambridge and Boston.
This expansion marked a significant step in enhancing connectivity between key urban centers, providing commuters with a faster and more efficient mode of transportation.
Expansion of the Orange Line (1987)
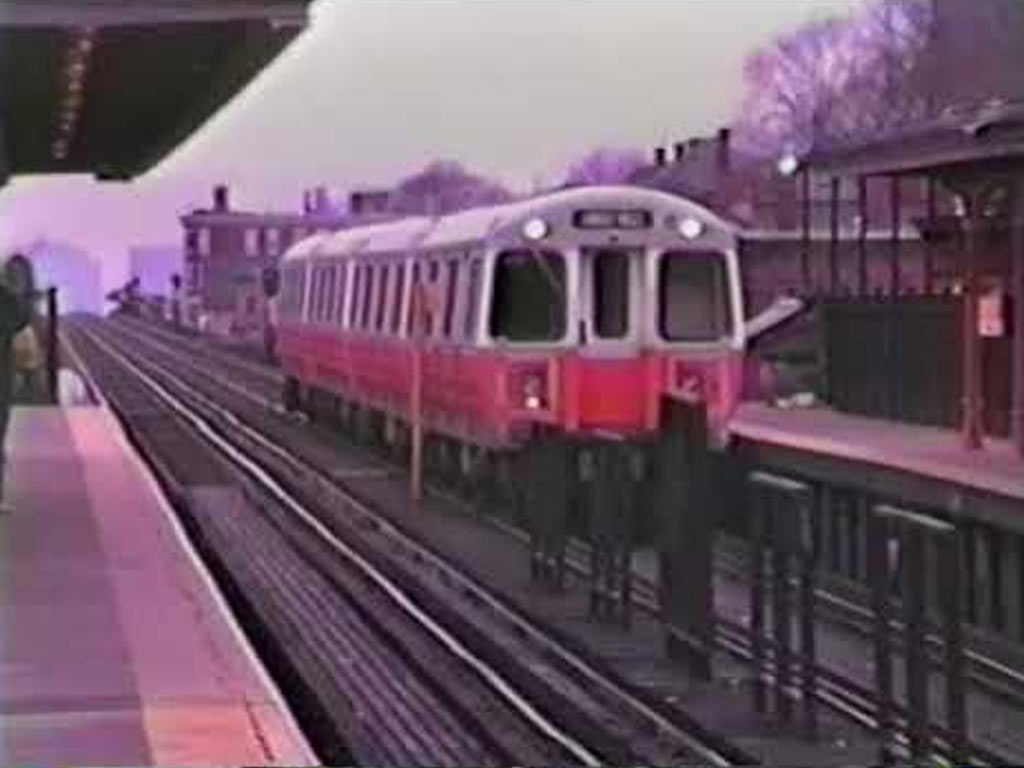

The Orange Line underwent a major transformation in 1987 with the opening of a new alignment.
This expansion not only improved the reliability and capacity of the line but also contributed to the modernization of the MBTA’s subway network, addressing the evolving needs of the growing population.
Commuter Rail Expansion (1990s)
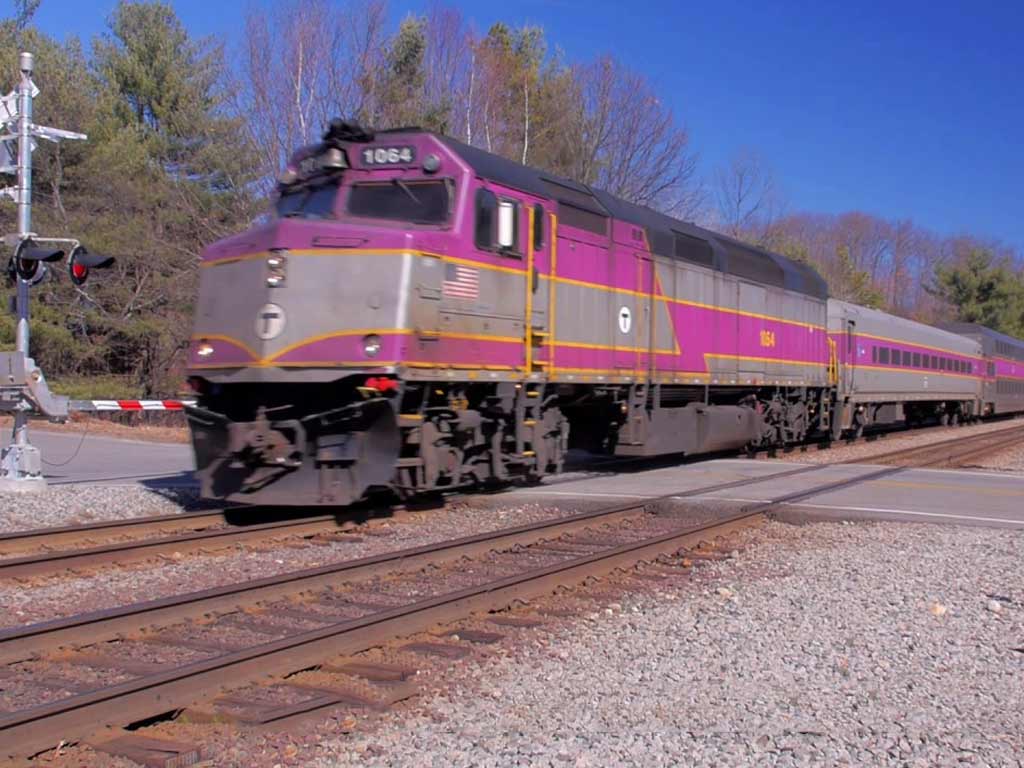

The 1990s witnessed significant expansion of the MBTA’s commuter rail services, introducing new lines and increasing connectivity to suburban areas.
This era marked a strategic effort to accommodate the commuting patterns of the region’s residents, fostering accessibility and reducing reliance on private vehicles.
Green Line Extension Project (2021)
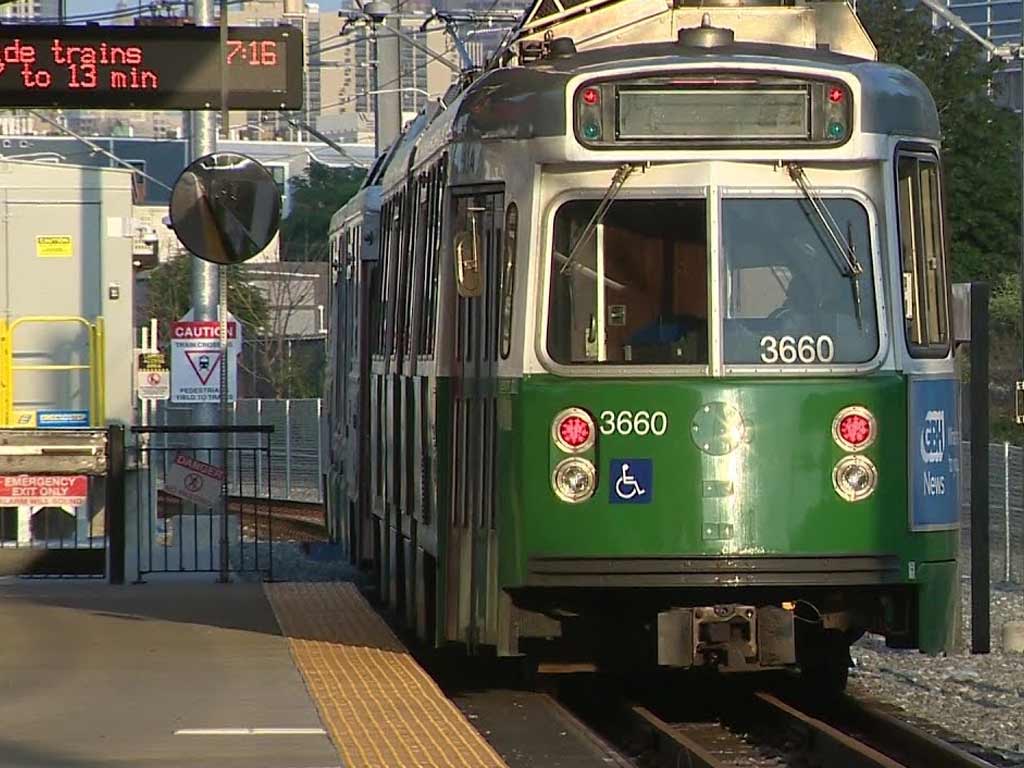

In recent history, the Green Line Extension Project has been a monumental endeavor aimed at extending the Green Line into Somerville and Medford.
Initiated to enhance public transit options and address growing urbanization, this project represents the MBTA’s commitment to adapting to the changing needs of the communities it serves.
Implementation of the Automated Fare Collection System (AFC) – 2006
In 2006, the MBTA implemented the Automated Fare Collection System, introducing electronic fare payment methods such as the CharlieCard.
This technological advancement streamlined the fare collection process, enhancing efficiency and providing commuters with more convenient and modern payment options.
Silver Line Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) Expansion – 2002 and 2004

The early 2000s saw the expansion of the Silver Line Bus Rapid Transit system, connecting South Boston to the city’s downtown and the airport.
This project aimed to improve accessibility to key areas, providing residents and visitors with a swift and reliable bus transit option.
Launch of The RIDE Paratransit Service – 1977

In 1977, the MBTA launched The RIDE, a paratransit service designed to meet the needs of individuals with disabilities.
This service has since played a crucial role in ensuring accessible transportation for all members of the community, fostering inclusivity in the MBTA’s transit offerings.
Creation of the MBTA Advisory Board – 1973
In 1973, the MBTA Advisory Board was established, providing a platform for municipalities served by the MBTA to have a voice in decision-making processes.
This collaborative approach reflected the importance of community engagement and feedback in shaping the evolution of public transportation services.
Forward Funding Legislation – 2000
The introduction of the Forward Funding legislation in 2000 marked a significant financial reform for the MBTA.
This legislation shifted the funding responsibility from annual legislative appropriations to a dedicated revenue stream, providing greater financial stability and enabling long-term planning for the MBTA’s infrastructure and service improvements.
These additional historical milestones underscore the MBTA’s commitment to innovation, accessibility, and responsiveness to the ever-changing needs of the Greater Boston community.
As the MBTA continues to evolve, these milestones serve as markers of its enduring impact on the region’s transportation and connectivity.
Launch of the MBTA Late-Night Service – 2014

In 2014, the MBTA initiated a late-night service, extending subway and key bus routes’ operational hours on weekends.
This step aimed to accommodate the diverse schedules of the city’s residents and visitors, enhancing accessibility during non-traditional commuting hours.
Inauguration of the Fairmount Line Improvements – 2019
The Fairmount Line, an essential commuter rail route, underwent substantial improvements in 2019.
This initiative included station upgrades, increased service frequency, and community engagement efforts, fostering equitable transit options for neighborhoods along the Fairmount Corridor.
Green Line Transformation (GLT) Program – Ongoing

The Green Line Transformation Program is an ongoing initiative focused on modernizing and expanding the Green Line, addressing key infrastructure needs, and enhancing overall service reliability.
This program underscores the MBTA’s commitment to adapting to evolving urban demands.
Response to COVID-19 Pandemic – 2020
In response to the global COVID-19 pandemic, the MBTA implemented various safety measures, including enhanced cleaning protocols, reduced service frequency, and the promotion of contactless payment.
These swift adaptations showcased the MBTA’s resilience and dedication to ensuring the safety of passengers and staff.
Introduction of AFC 2.0 and Fare Transformation – 2023
Anticipated in 2023, the introduction of AFC 2.0 marks a pivotal moment in the MBTA’s history.
This fare payment system upgrade aims to enhance user experience, streamline fare collection processes, and incorporate new technologies, aligning with the authority’s commitment to technological innovation.
These additional milestones underscore the MBTA’s responsiveness to the evolving needs of the Greater Boston community and its proactive approach to creating a transit system that is both adaptable and forward-thinking.
As the MBTA continues its journey, these historical markers contribute to the ongoing narrative of progress and improvement within the realm of public transportation.
Faqs
What was the initial scope of the MBTA’s transit services?
The MBTA’s initial scope included bus, subway, and commuter rail services. This consolidation aimed to provide a comprehensive and integrated public transportation system serving the diverse needs of the Greater Boston community.
How has the MBTA evolved its subway system over the years?
The MBTA’s subway system has evolved through expansions, such as the introduction of the Red Line in 1965 and the transformation of the Orange Line in 1987. These initiatives aimed to enhance connectivity and modernize the subway network.
What role did the MBTA play in commuter rail expansion during the 1990s?
In the 1990s, the MBTA significantly expanded its commuter rail services, introducing new lines and enhancing connectivity to suburban areas. This expansion addressed growing commuting patterns and increased accessibility to outlying regions.
How did the MBTA respond to financial challenges in 2000?
In 2000, the MBTA underwent a significant financial reform with the introduction of the Forward Funding legislation. This legislative change shifted funding responsibility to a dedicated revenue stream, providing greater financial stability for long-term planning and improvements.
What are some recent milestones in the history of the MBTA?
Recent milestones include the launch of late-night services in 2014, improvements to the Fairmount Line in 2019, and ongoing projects like the Green Line Transformation Program.
These initiatives reflect the MBTA’s commitment to adapting to contemporary needs and enhancing its services.
Conclusion
The history of the MBTA stands as a testament to the vital role of public transportation in fostering connectivity and community development.
From its inception in 1964 to ongoing initiatives and innovations, the MBTA has navigated the complex landscape of Greater Boston’s transportation needs with adaptability and foresight.
As the MBTA continues to evolve, each historical milestone contributes to a legacy of progress, resilience, and service.
The authority’s commitment to enhancing accessibility, embracing technological advancements, and responding to the diverse needs of its riders underscores the enduring importance of the MBTA in shaping the dynamic tapestry of transportation history in the Greater Boston area.
Jaclyn Lowe