Salem, Massachusetts’s enigmatic and glorious history unfolds as a captivating tale of intrigue, prosperity, and tragedy.
Salem’s story is etched with layers of complexity and cultural richness, from its colonial origins to its infamous witch trials and maritime prowess.
This historic city, nestled along the coast of Massachusetts, holds a unique place in American lore, drawing visitors from around the world to explore its intriguing past.
As we delve into Salem’s history, we unravel the mysteries of its colonial heritage, marvel at its maritime achievements, and contemplate the darker chapters, such as the Salem Witch Trials.
Through its enigmatic narrative, Salem invites us to ponder the complexities of human nature, resilience, and the enduring legacy of a city steeped in both glory and infamy. Stay focused.
The Early Settlement in Salem, Massachusetts History
The early settlement of Salem, Massachusetts, holds a significant place in American history, marked by the arrival of Roger Conant and his associates in 1626.
These pioneers laid the foundation for a community later known for its pivotal role in colonial America, particularly during the infamous Salem Witch Trials.
Here, we delve into the key aspects of Salem’s early settlement and its historical significance.
Establishment by Roger Conant

In 1626, Roger Conant and a group of settlers arrived from Cape Ann, establishing the first permanent settlement in Salem.
Their decision to settle in Salem was influenced by its strategic location for fishing and trade, providing access to abundant natural resources.
The leadership of Captain John Endicott
In 1628, Captain John Endicott led a larger group of settlers to Salem, further solidifying its status as a burgeoning colonial settlement.
Endicott played a crucial role in governing the early community and establishing order amidst the challenges of frontier life.
Cultural Exchange with Indigenous Peoples
The indigenous name for the area, Naumkeag, reflects the presence of Native American tribes in the region prior to European settlement.
Early settlers engaged in trade and diplomatic relations with indigenous peoples, contributing to a complex cultural exchange.
Economic Growth and Development
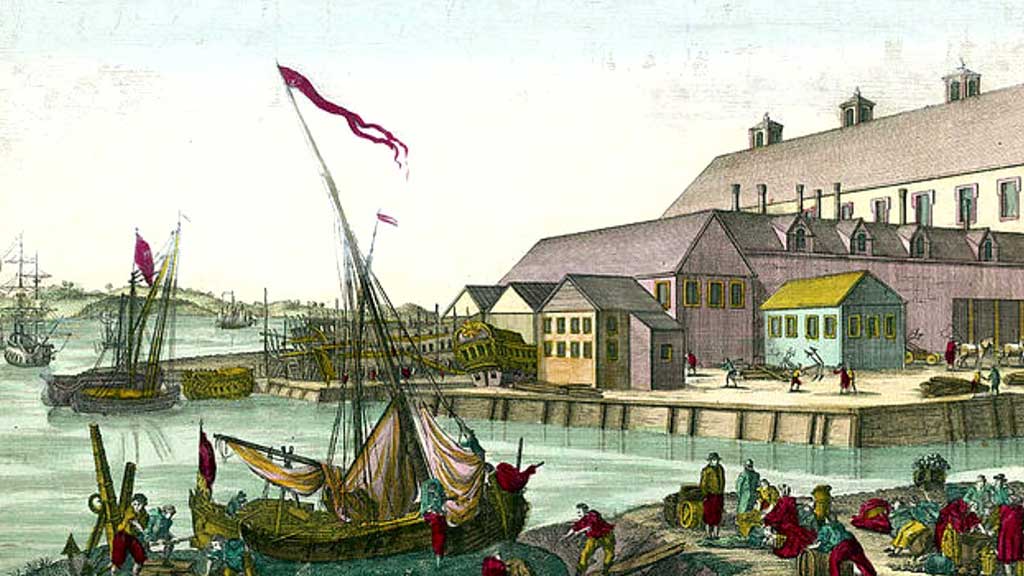
Salem’s proximity to the sea facilitated the growth of maritime industries such as fishing, shipping, and shipbuilding.
Establishing trade routes with Europe and the Caribbean bolstered Salem’s economy, leading to prosperity and expansion.
Religious and Social Dynamics
The early settlers of Salem were primarily Puritans seeking religious freedom and refuge from persecution in England.
Puritan values and beliefs shaped the social fabric of Salem, influencing governance, education, and community life.
The early settlement of Salem, Massachusetts, represents a pivotal chapter in American colonial history, characterized by exploration, resilience, and cultural exchange.
Salem emerged as a vibrant hub of trade, commerce, and religious fervour from its humble beginnings under Roger Conant to the leadership of figures like Captain John Endicott.
Overview of the Infamous Salem Witch Trials in 1692
The Salem Witch Trials of 1692 represent one of the most infamous episodes in American colonial history, marked by hysteria, paranoia, and tragedy. Here’s an overview of this dark chapter:
Background and Context

Salem Village (now Danvers, Massachusetts) was a Puritan community deeply rooted in religious beliefs and social hierarchy.
Tensions were high due to economic hardships, social divisions, and fears of Native American attacks during King William’s War.
The Puritans held strong beliefs in the supernatural and witchcraft, viewing it as a grave threat to their religious and moral order.
Outbreak of Accusations
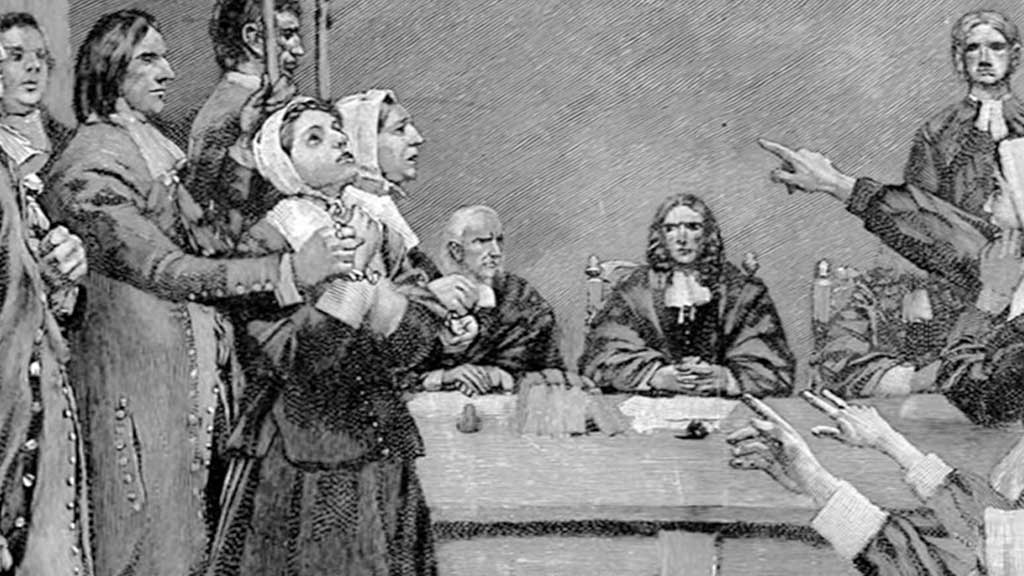
The hysteria began in January 1692 when a group of young girls, including Betty Parris and Abigail Williams, exhibited strange behaviour, which was attributed to witchcraft.
The girls accused three women of bewitching them: Tituba, a Caribbean slave; Sarah Good, a homeless woman; and Sarah Osborne, an elderly widow.
Trials and Executions
The accusations triggered a wave of arrests and trials, with the accused facing harsh interrogation and pressure to confess.
The trials lacked due process, relying heavily on spectral evidence (testimony about dreams and visions) and coerced confessions.
Over the course of several months, 19 people were hanged, including women like Bridget Bishop, Rebecca Nurse, and Martha Corey, while one man, Giles Corey, was pressed to death.
Several others languished in jail, and many more faced accusations and social ostracism.
Impact and Aftermath
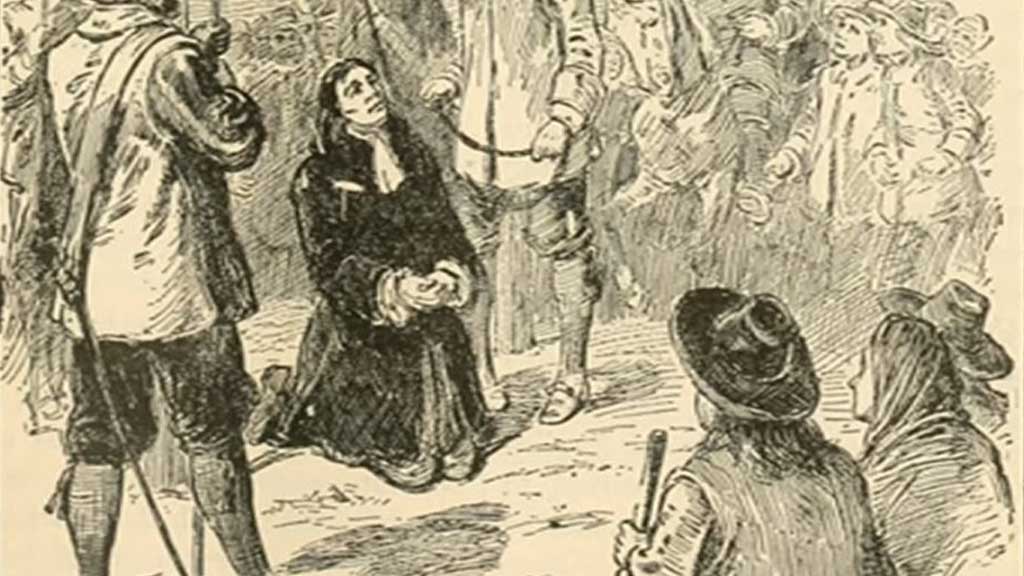

The Salem Witch Trials exposed the dangers of mass hysteria, prejudice, and the abuse of power.
The trials shattered the community’s trust and divided families and neighbours.
In the aftermath, there was a growing scepticism towards spectral evidence and a reevaluation of the legal standards for witchcraft accusations.
The trials left a lasting scar on American history, serving as a cautionary tale about the consequences of unchecked fear and intolerance.
Legacy and Cultural Impact
The Salem Witch Trials continue to captivate public imagination, inspiring numerous literary works, plays, and films exploring themes of justice, hysteria, and the human psyche.
The events of 1692 have also sparked scholarly debate and research into the social, cultural, and psychological factors that contributed to the hysteria.
Maritime Trade and Prosperity in Salem, Massachusetts History
Maritime trade played a pivotal role in the prosperity and development of Salem, Massachusetts, during the 17th and 18th centuries. Here’s an overview of the maritime trade and its impact on Salem’s history:
Geographic Advantage

Salem’s strategic location along the coast of Massachusetts provided easy access to the Atlantic Ocean, making it an ideal port for maritime trade.
The city’s deep harbour and proximity to major trade routes facilitated the growth of shipping and commerce.
Trading Ventures
Salem merchants engaged in various trading ventures, including importing and exporting goods such as fish, timber, rum, molasses, sugar, textiles, and spices.
Salem’s merchants established lucrative trade routes with Europe, the Caribbean, Africa, and Asia, importing luxury goods and raw materials while exporting New England products.
Triangle Trade
Salem participated in the Triangle Trade, a transatlantic trade network that involved the exchange of goods, slaves, and raw materials between Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
Salem’s merchants profited from the trade of rum, which was produced locally from Caribbean molasses and exported to Africa to be exchanged for slaves, who were then transported to the Americas.
Shipbuilding Industry

The maritime trade boom fueled the growth of Salem’s shipbuilding industry, with numerous shipyards established along the waterfront.
Salem became known for producing fast and sturdy vessels, including merchant ships, privateers, and even some of the earliest American naval ships.
Economic Prosperity
Maritime trade brought unprecedented wealth and prosperity to Salem, transforming it from a small fishing village into one of the wealthiest cities in colonial America.
The profits from trade enabled Salem’s merchants to invest in grand mansions, elegant gardens, and luxurious lifestyles, creating a vibrant social and cultural scene in the city.
Cultural Exchange and Influence
Maritime trade brought Salem into contact with people and cultures worldwide, fostering a rich exchange of ideas, goods, and customs.
The city’s diverse population, which included merchants, sailors, immigrants, and enslaved Africans, contributed to its cosmopolitan character and cultural diversity.
Maritime trade was the lifeblood of Salem, Massachusetts, driving its economic growth, cultural exchange, and prosperity during the colonial period.
Industrialization in Salem, Massachusetts History
Industrialization significantly shaped the history of Salem, Massachusetts, particularly during the 19th century. Here’s an overview of industrialization in Salem:
Early Industrial Development
Salem’s industrialization began in the late 18th century with the establishment of small-scale manufacturing enterprises, including textile mills, tanneries, and rope-making factories.
These early industries took advantage of Salem’s abundant waterways for power and transportation.
Textile Manufacturing
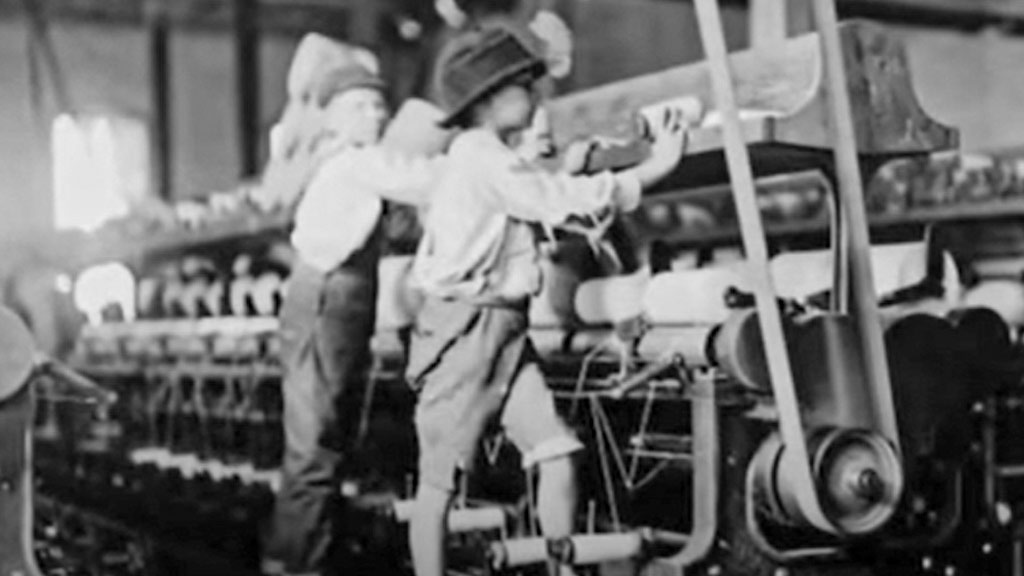

Textile manufacturing emerged as one of the leading industries in Salem during the early 19th century.
The construction of textile mills along the city’s rivers and streams led to the mass production of textiles, including cotton, wool, and silk fabrics.
Salem’s textile mills employed a large workforce, including women and children, and contributed significantly to the city’s economic growth.
Leather and Shoe Industry
Salem became a centre for leather production and shoemaking, with numerous tanneries and shoe factories established in the city.
Salem’s leather and shoe industry thrived due to its proximity to abundant raw materials, such as hides and timber, and access to skilled labour.
Maritime Industries
While industrialization transformed Salem’s economy, maritime industries played a vital role in the city’s economy.
Shipbuilding remained an important industry, albeit on a smaller scale, with shipyards producing vessels for coastal trade and fishing.
Technological Innovation
The industrialization of Salem was characterized by technological advancements and innovations.
The introduction of steam power revolutionized manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity in Salem’s factories and mills.
Urban Growth and Transformation
Industrialization fueled urban growth and transformation in Salem by expanding factory complexes, worker housing, and infrastructure.
The population of Salem grew rapidly as workers migrated to the city in search of employment opportunities in the burgeoning industrial sector.
Social and Environmental Impact
Industrialization brought both opportunities and challenges to Salem. While it stimulated economic growth and prosperity, it also led to social inequalities, labour exploitation, and environmental degradation.
Workers in Salem’s factories and mills faced harsh working conditions, long hours, and low wages, sparking labour unrest and calls for reform.
Industrialization profoundly transformed the economy, society, and landscape of Salem, Massachusetts, during the 19th century, shaping its identity as a centre of manufacturing and commerce in New England.
Cultural Heritage of Salem in Massachusetts
The cultural heritage of Salem, Massachusetts, is rich and diverse, encompassing a wide range of historical, artistic, and literary traditions. Here’s an overview of Salem’s cultural heritage:
Colonial History
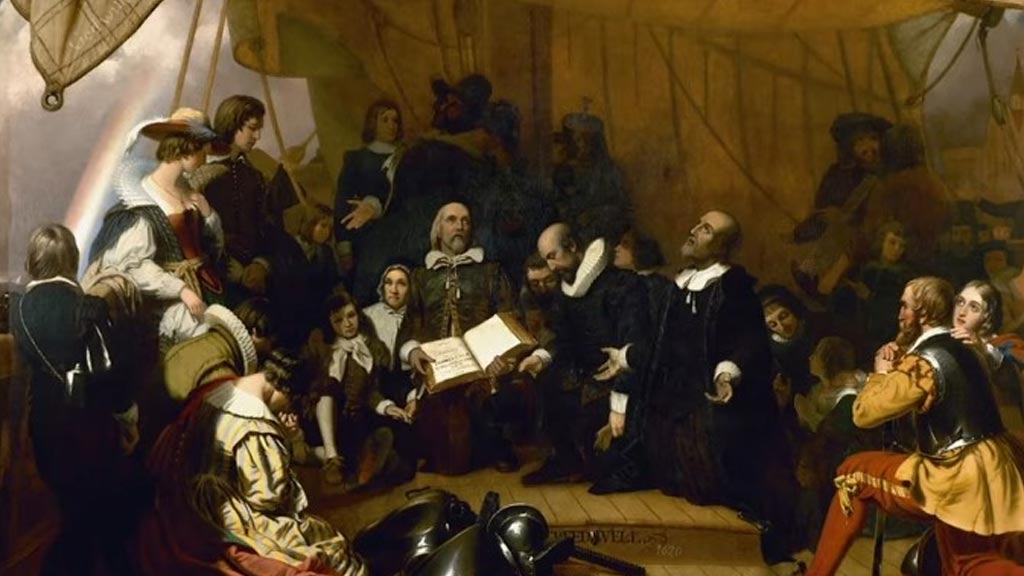

Salem’s colonial history is a significant part of its cultural heritage, characterized by its early settlement by Puritans in the 17th century and its role as a major seaport and trading hub.
Historic sites such as the Salem Maritime National Historic Site, the House of the Seven Gables, and the Salem Witch Trials Memorial preserve and interpret Salem’s colonial past.
Maritime Legacy
Salem’s maritime heritage is deeply ingrained in its culture, stemming from its history as a prominent seaport and shipbuilding centre.
The Salem Maritime National Historic Site, including historic wharves, warehouses, and ships, celebrates Salem’s maritime legacy and contributions to American commerce and exploration.
Witchcraft and Halloween
Salem is perhaps best known for its association with the infamous Salem Witch Trials of 1692, which have left a lasting imprint on the city’s cultural identity.
Each year, Salem attracts thousands of visitors worldwide who come to explore its witchcraft-related attractions, museums, and events, particularly during the Halloween season.
Arts and Literature
Salem has a vibrant arts and literary community inspired by its rich history and cultural heritage.
The city is home to numerous art galleries, museums, and cultural institutions, including the Peabody Essex Museum, which showcases a diverse collection of art and artefacts reflecting Salem’s global connections.
Salem has also been the setting for numerous works of literature and film, including Nathaniel Hawthorne’s “The Scarlet Letter” and Arthur Miller’s play “The Crucible,” drawing on Salem’s colonial history and the witch trials.
Architecture and Historic Preservation
Salem boasts a wealth of historic architecture, ranging from colonial-era homes and Federal-style mansions to Victorian-era buildings and Gothic Revival churches.
Preserving Salem’s historic buildings and neighbourhoods is central to its cultural heritage, with organizations such as Historic Salem, Inc. working to protect and promote the city’s architectural legacy.
Ethnic and Immigrant Heritage
Salem’s cultural heritage is also shaped by its diverse ethnic and immigrant communities, including descendants of early European settlers and more recent arrivals from countries such as Ireland, Italy, and Eastern Europe.
Festivals, celebrations, and cultural events throughout the year highlight Salem’s multicultural heritage and traditions.
The cultural heritage of Salem, Massachusetts, is multifaceted and dynamic, reflecting its rich history, maritime legacy, literary heritage, and diverse community.
FAQs
What role did Salem play in the colonial era?
Salem was a significant seaport and trading hub in the colonial era, engaging in maritime commerce with Europe, the Caribbean, and beyond.
Its prosperous economy was fueled by industries such as shipbuilding, fishing, and trade, shaping its cultural and economic landscape.
What were the Salem Witch Trials, and when did they occur?
The Salem Witch Trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts, primarily in 1692.
The trials resulted in the execution of 20 individuals and left a lasting mark on American history, highlighting the dangers of mass hysteria and prejudice.
How did Salem’s maritime trade contribute to its prosperity?
Salem’s strategic location and thriving maritime trade facilitated economic growth and prosperity during the colonial era.
The city’s merchants traded with Europe, the Caribbean, and Asia, importing luxury goods and exporting New England products, which fueled the city’s wealth and expansion.
What are some notable landmarks related to Salem’s history?
Salem boasts several notable landmarks in its rich history, including the Salem Maritime National Historic Site, the House of the Seven Gables, the Witch House, and the Salem Witch Trials Memorial.
These sites preserve and interpret Salem’s colonial past and cultural heritage.
How has Salem’s cultural heritage influenced its modern identity?
Salem’s cultural heritage, including its colonial history, maritime legacy, and association with the Salem Witch Trials, continues to shape its modern identity.
The city’s vibrant arts scene, historic preservation efforts, and tourism industry reflect its rich and diverse cultural heritage, attracting visitors worldwide.
Wrapping Up
Salem, Massachusetts, stands as a testament to the complexity and richness of American history.
The city’s cultural heritage is a tapestry woven with diverse threads of tradition, innovation, and resilience, from its colonial origins and maritime trade to the infamous Salem Witch Trials.
As Salem continues to evolve and embrace its past, its historical landmarks, cultural institutions, and vibrant community remind us of the enduring legacy of one of America’s most fascinating cities. Best of luck.
Jaclyn Lowe