Boston holds paramount importance in American history due to its pivotal role in shaping the nation’s early foundations and contributing significantly to its evolution.
As one of the oldest cities in the United States, Boston’s historical narrative is intertwined with key moments that shaped the course of American history.
Boston’s significance is multifaceted, from being a crucible of revolutionary sentiments during the American Revolution to its economic and cultural hub role.
The city’s legacy includes hosting events like the Boston Tea Party and the Battles of Lexington and Concord and establishing educational institutions like Harvard University.
This introduction delves into Boston’s profound impact on the emergence of the United States, offering a glimpse into its rich historical tapestry that continues to captivate those seeking to understand the roots of the American story.
Early Colonial Roots of Boston in America
Boston, one of the oldest cities in the United States, has deep colonial roots that date back to the early 17th century.
The city’s history is closely tied to the arrival of the Pilgrims and Puritans, who sought religious freedom and established the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Here are key aspects of the early colonial roots of Boston:
Puritan Settlements
In 1620, the Pilgrims arrived on the Mayflower and established the Plymouth Colony, south of Boston.
Later, in 1630, a larger wave of Puritans, led by Governor John Winthrop, arrived and settled north of Plymouth, establishing the Massachusetts Bay Colony.
The Puritans were a group of English Protestants who sought to reform the Church of England. They faced religious persecution in England and sought a new home in the New World.
Founding of Boston
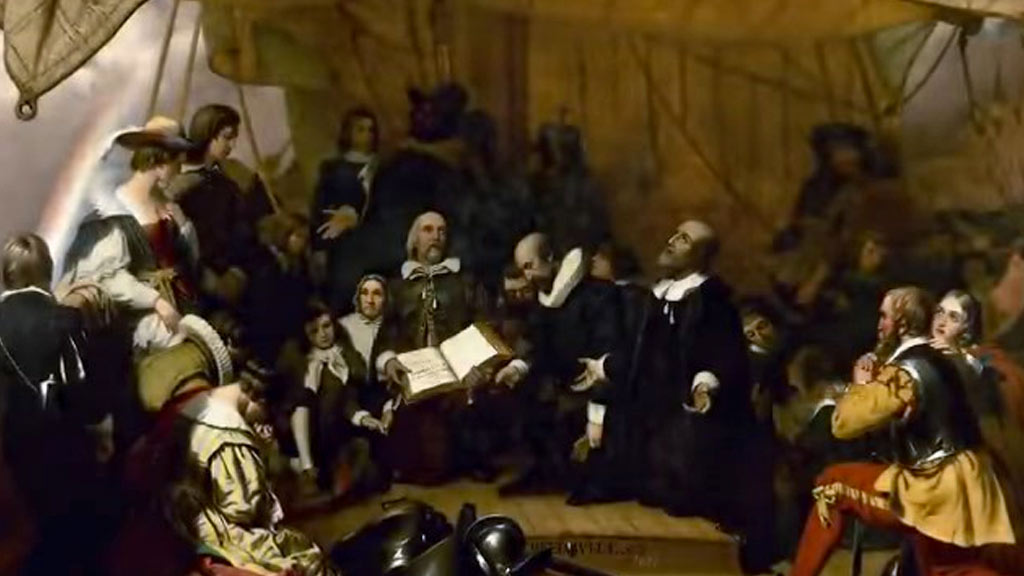

In 1630, the Puritans founded the settlement of Shawmut, which would later become Boston. The name Boston was inspired by the town of Boston in Lincolnshire, England.
The early settlers faced numerous challenges, including harsh weather conditions, but they were determined to create a community based on their religious principles.
The Great Migration
The 1630s saw a significant influx of Puritans to the Massachusetts Bay Colony, known as the Great Migration. Thousands of settlers seeking religious freedom and economic opportunities arrived in the region during this period.
Religious Influence
The Puritans played a central role in shaping early Boston’s religious and social character.
The Massachusetts Bay Colony was governed by strict Puritan principles, and the leaders sought to create a “City upon a Hill,” a model community guided by moral and religious values.
Economic Development
Boston’s natural harbour and proximity to fertile land facilitated economic growth. Fishing, trade, and agriculture became vital aspects of the local economy.
The town quickly became a centre for commerce and attracted merchants and tradespeople.
Educational Institutions
Education was highly valued among the Puritans, who established schools to ensure the proper education of their children.
In 1636, Harvard College was founded in nearby Cambridge, making it the oldest institution of higher education in the United States.
Tensions and Conflicts
Despite the idealistic goals of the Puritans, conflicts arose within the colony, leading to the expulsion of dissenting individuals such as Anne Hutchinson and Roger Williams.
These tensions contributed to the diversification of settlements in the region. Boston’s early colonial roots set the stage for its future as a major centre of commerce, education, and cultural development.
The city played a crucial role in the American Revolution and has remained a significant cultural and economic hub throughout American history.
Why Is Boston Important in American History?
Boston is prominent in American history due to its pivotal role in several key events that shaped the nation. Here are some reasons why Boston is important in American history:
Pilgrims and Puritans
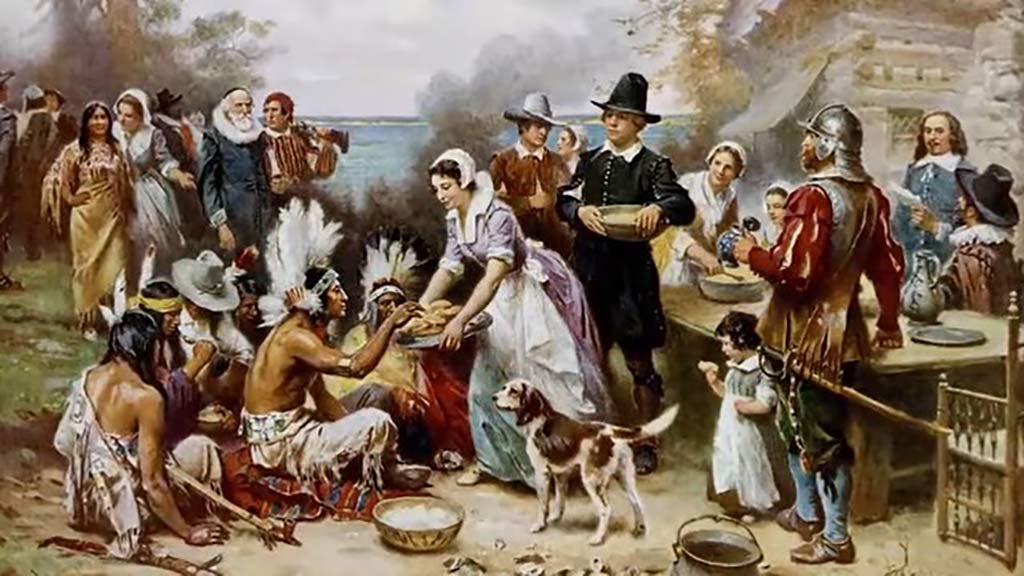

Boston was founded by Puritans in 1630, and its early colonial roots are deeply connected to the religious motivations of the Pilgrims and Puritans who sought refuge and religious freedom in the New World.
The establishment of the Massachusetts Bay Colony laid the foundation for the city’s historical significance.
American Revolution
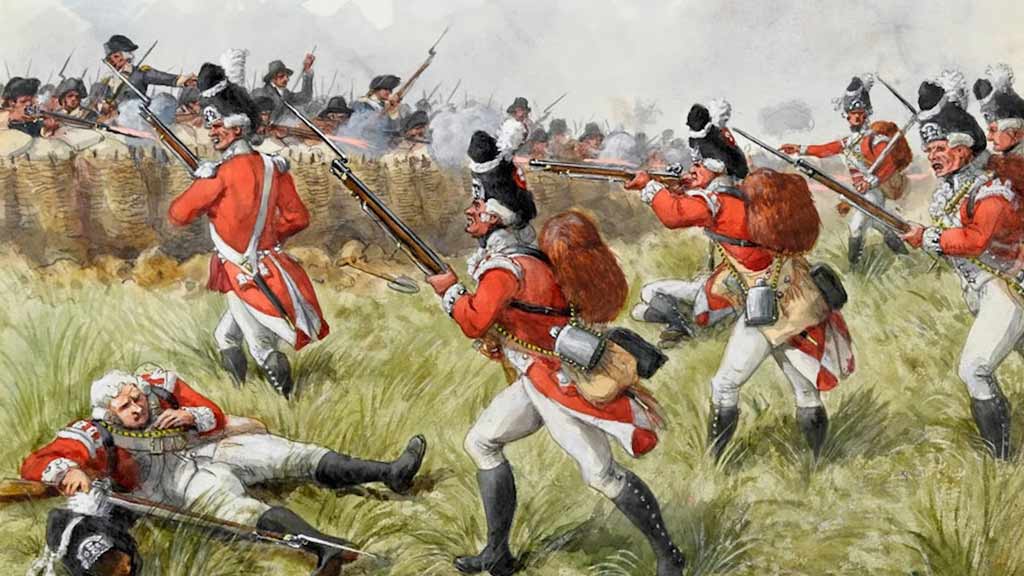

Boston played a central role in the lead-up to the American Revolution. The city witnessed events like the Boston Massacre in 1770 and the Boston Tea Party in 1773, both of which fueled tensions between the American colonists and British authorities.
The Battles of Lexington and Concord in 1775, often considered the beginning of the Revolutionary War, occurred in the vicinity of Boston.
The Siege of Boston followed, lasting from 1775 to 1776, and eventually led to the British evacuation from the city.
Boston Massacre
In 1770, tensions between British soldiers and colonists reached a breaking point, resulting in the Boston Massacre.
British troops fired into a crowd of colonists, leading to several deaths. This incident further fueled anti-British sentiment and increased the desire for independence.
Boston Tea Party
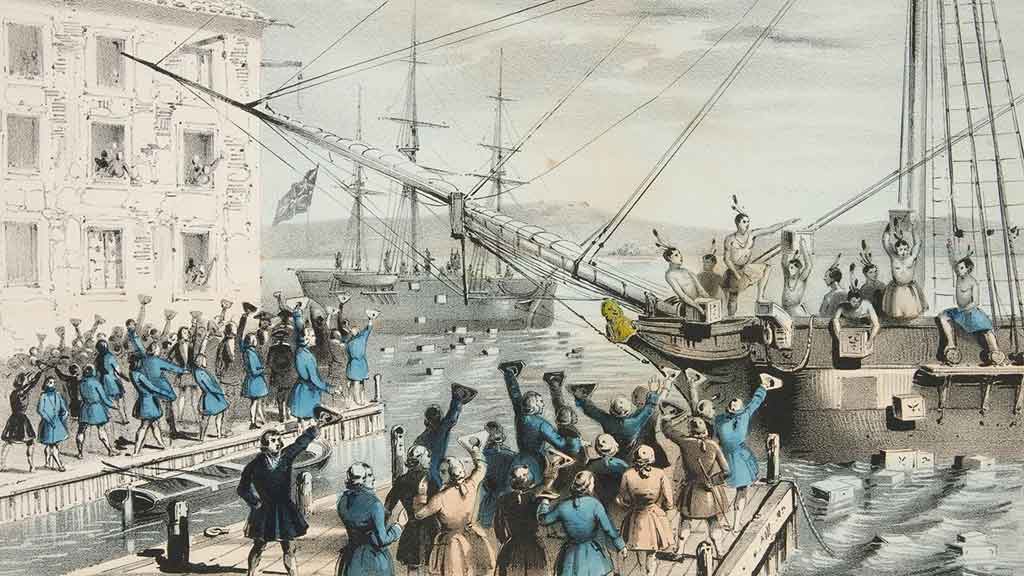
In 1773, colonists, angered by British taxation without representation, staged the Boston Tea Party. They dumped crates of tea into Boston Harbor in protest against the Tea Act.
This event symbolized resistance to British rule and became a rallying cry for American independence.
Siege of Boston
Following the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the Siege of Boston took place, with American forces surrounding the city.
It was a crucial early military engagement in the Revolutionary War and eventually led to the British evacuation of Boston in 1776.
Birth of the United States Navy
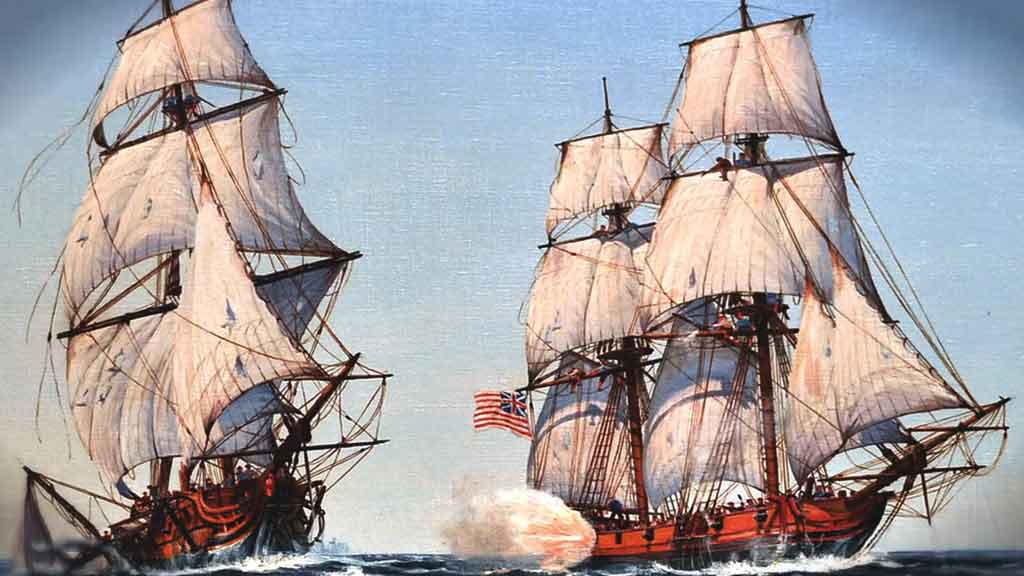
During the Revolutionary War, the first official flag of the United States, the Grand Union Flag, was raised on the USS Alfred, a ship commissioned in Boston Harbor.
This event is considered a significant moment in establishing the United States Navy.
Cultural and Educational Hub
Boston has long been a centre of education and culture. It is home to Harvard University, founded in nearby Cambridge in 1636, and numerous other prestigious institutions.
The city has played a crucial role in the intellectual and academic development of the United States.
Industrial and Economic Growth
In the 19th century, Boston became an industrial and economic growth hub. Industries such as textiles, manufacturing, and shipping thrived, contributing to the city’s economic significance.
Immigration and Diversity
Boston has been shaped by waves of immigration, from Irish immigrants in the 19th century to more recent waves of immigrants from various parts of the world.
This diversity has enriched the city’s culture and contributed to its dynamic character.
Modern Political and Cultural Influence
Boston continues to play a significant role in American politics and culture. It has been a hub for social and political movements, and its historical sites attract millions of visitors interested in understanding the nation’s origins.
Boston’s importance in American history stems from its role in the early colonial period, the Revolutionary War, its cultural and educational contributions, and its ongoing impact on American politics and society.
The city’s historical legacy is deeply intertwined with the broader narrative of the United States.
Boston as the Economic and Industrial Powerhouse in America
While Boston has a rich history as a cultural and educational centre, it also played a significant role as an economic and industrial powerhouse in the United States during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Several factors contributed to Boston’s economic and industrial success:
Trade and Commerce
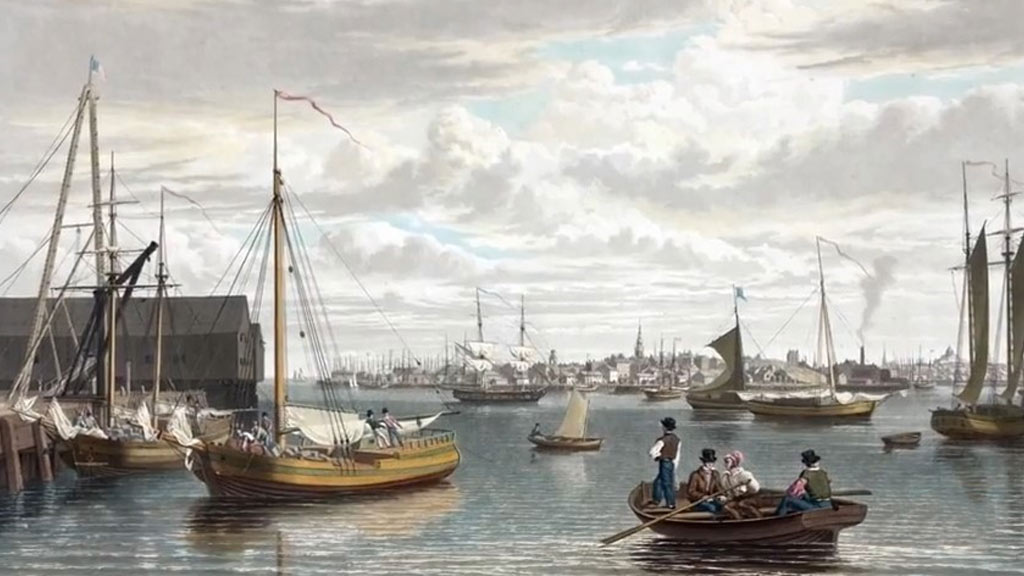

Boston’s natural harbour made it a strategic port for trade. The city’s merchants engaged in international trade, facilitating the exchange of goods with Europe, the Caribbean, and other parts of the world. The maritime trade contributed to the city’s economic growth.
Shipping and Maritime Industry
Boston’s economy thrived on maritime activities, including shipbuilding, shipping, and fishing. The city’s shipyards produced a significant number of vessels, and its sailors were involved in global trade routes.
Manufacturing and Industry
During the 19th century, Boston experienced industrialization and the growth of manufacturing. Industries such as textiles, shoemaking, and machinery production became prominent.
The city’s factories and mills contributed to the overall industrial development of the region.
Innovation and Technology
Boston was at the forefront of technological innovation. The city’s industries embraced new manufacturing techniques and machinery, contributing to advancements in various sectors.
This commitment to innovation laid the groundwork for future economic growth.
Financial Center
Boston emerged as a financial centre, establishing banks and financial institutions.
The city’s financial sector was crucial in supporting industrial and commercial activities, providing the necessary capital for expanding businesses.
Educational Institutions and Research
The presence of prestigious educational institutions, including Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), fostered a culture of research and development.
Boston’s intellectual capital contributed to advancements in science and technology, supporting innovation in various industries.
Transportation Infrastructure
Transportation infrastructure development, including railroads and later highways, further enhanced Boston’s economic prowess. Improved connectivity facilitated the movement of goods and people, supporting trade and industry.
Diverse Economy
Boston’s economy was diverse, with various industries contributing to its success. The city was not reliant on a single sector, allowing it to weather economic fluctuations and adapt to changing market conditions.
Labor Force and Immigration
The influx of immigrants, particularly in the 19th century, provided a skilled and diverse labour force. Immigrants brought their expertise to various industries, contributing to the city’s economic vibrancy.
Cultural and Intellectual Capital
Boston’s cultural and intellectual environment attracted talent and entrepreneurs. The city became a hub for innovation, with a concentration of skilled workers and professionals contributing to its economic strength.
While Boston’s economic landscape has evolved over time, transitioning to a more service-oriented and technology-driven economy in recent decades.
The city’s industrial and economic prowess during the 19th and early 20th centuries was crucial in shaping its legacy as a major American city.
FAQs
How did Boston contribute to the formation of the United States?
Boston played a crucial role in the American Revolution, witnessing key events like the Boston Massacre and the Siege of Boston.
The city’s resistance to British rule and its significance in early revolutionary activities contributed to the formation and spirit of the United States.
What educational institutions in Boston have influenced American history?
Harvard University, founded in 1636, is a key institution in Boston that has shaped American intellectual history.
Its long-standing influence and other prestigious universities in the city have contributed significantly to the nation’s educational and cultural development.
How did Boston’s economic activities impact American history?
Boston emerged as a maritime and industrial powerhouse in the 19th century. Its bustling trade, shipping, and manufacturing sectors played a vital role in shaping the nation’s economic landscape.
The city’s economic prowess contributed to the overall growth and prosperity of the United States.
What cultural and historical sites in Boston attract visitors interested in American history?
Boston boasts numerous historical sites, including the Freedom Trail, Paul Revere’s House, and the USS Constitution.
These landmarks connect to the city’s rich history, attracting visitors worldwide who seek to explore and understand America’s early colonial and revolutionary roots.
Wrapping Up
Boston’s significance in American history is profound, rooted in its role as a cradle of liberty during the Revolutionary War, its impact on the formation of the United States, its educational and cultural contributions, and its economic prowess.
Boston has left an indelible mark on the nation’s narrative from the early colonial period to the American Revolution and beyond.
The city’s historical legacy is etched in events like the Boston Tea Party, the Siege of Boston, and the cultural and intellectual capital fostered by institutions like Harvard University.
As a maritime and industrial powerhouse, Boston shaped the economic trajectory of the United States in the 19th century.
Today, its historical sites continue to attract visitors, offering a tangible connection to America’s roots and a deeper understanding of the city’s enduring impact on the nation.
Jaclyn Lowe